Background Handling
While a user has joined a 100ms Room they can put the app in Background Mode & usually expect a certain subset of app functionality continues to work.
Background Mode implies that the application is not currently visible to the user, not responding to user input, and running in the Background.
Background state in Flutter apps is represented by AppLifecycleState.paused as described here.
Android & iOS have different mechanisms of handling app behaviour which includes limiting access to Camera & Microphone, time allowed to keep running before getting completely stopped, Aggressive Battery Optimisations on Android OEMs, etc.
There are 2 prominent behaviours that are mainly affected when apps transition to Background State - Publishing Audio/Video, and Playing incoming Audio/Video.
Let's breakdown how your apps can implement efficient handling of Background states on iOS & Android Platforms.
How to prevent mobile device from getting locked while on a call?
To prevent the device from locking during lengthy video or audio calls, you can utilize the toggleAlwaysScreenOn api. By default, devices are configured to lock the screen after a certain period of inactivity as defined in the device settings. However, during calls, where user interactions on the screen are minimal, this behavior can become disruptive. To address this issue, the above API can be employed.
It allows you to acquire a wake lock, ensuring that the device remains awake and the screen stays active during the call. By utilizing this, you can prevent the device from locking automatically and provide a seamless call experience.
Managing Wakelock and Earpiece Audio Source in Your App
During phone calls, when using the Wakelock feature to keep the screen on, we often place our phones near our ears. However, this proximity sometimes results in unintentional button presses on the app, as the phone's screen comes into contact with our face. To handle such cases we will need to disable wakelock and enable the proximity sensor's default behaviour.
We can use the proximity_screen_lock package to enable this functionality. Just add this package in pubspec.yaml, run flutter pub get
and add the below code in your application to enable this:
if (ProximityLockScreen.isProximityLockSupported()) { ProximityLockScreen.setActive(true) }
iOS Background Handling
When your app goes into the background, by default it can no longer access camera or microphone and publish it to other peers in the room. Also, you cannot hear audio of other participants in the call if your app is in the background without enabling Background Modes.
This is the default iOS platform behaviour whereby it limits access to Microphone & Camera for capturing Audio & Video. By default, iOS also stops playing audio of the Room when your app is in Background.
By Enabling Background Modes you can ensure that your iOS app has access to Microphone & can play incoming Audio from the Room.
Following steps show how to add Background Modes in iOS:
Open project in Xcode
Open project in Xcode by right clicking on ios folder in project and select Open in Xcode as shown in image below.

Add Capability
Click on Runner in Navigator then select Runner under TARGETS and click on Signing & Capabilities and add Capability.

Background Mode
Search background mode and add it to project by clicking on it.

Enable Background Mode
Enable the checkbox under Background Modes named Audio, AirPlay, and Picture in Picture.
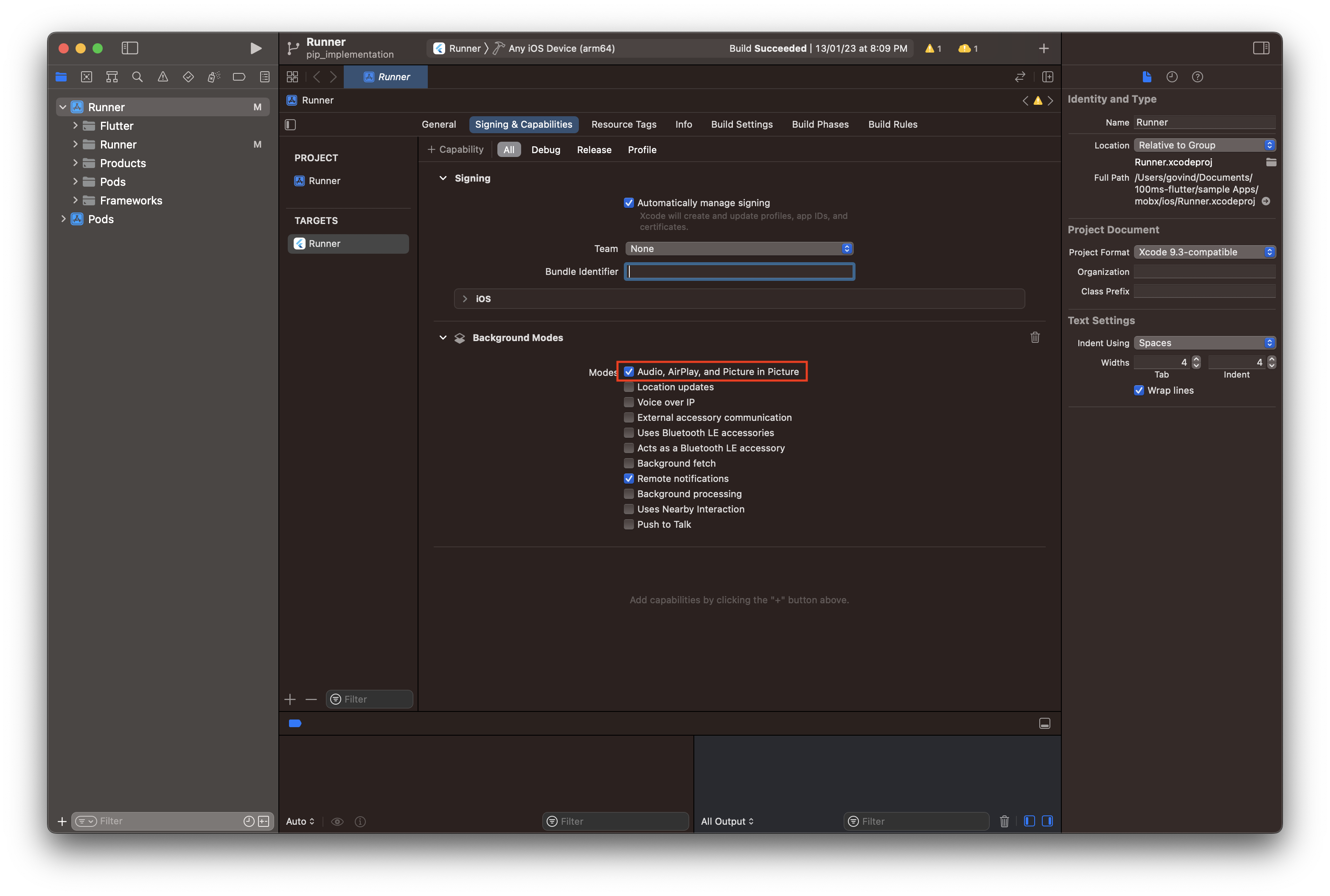
Let's look at different scenarios on iOS with & without Enabling Background Modes.
Without Background Modes Enabled (Default iOS Behaviour)
The table lists down iOS app behaviours when the app transitions to background when a 100ms Room is ongoing without enabling background processing.
The "Scenario" on the left of the Table below implies the activity which is ongoing in the App when user has joined a 100ms Room.
The "Behaviours" on the right of the Table shows what happens when the App transitions to Background.
| Scenario | Behaviours |
|---|---|
| Mic is Unmuted | Mic will get Muted |
| Camera is unmuted | Camera will get Muted |
| Remote Peers are publishing audio | Incoming Audio from Room Stops Playing |
Background Modes Enabled (Recommended)
The table lists down iOS app behaviours when the app transitions to background when a 100ms Room is ongoing with Background Modes Enabled.
The "Scenario" on the left of the Table below implies the activity which is ongoing in the App when user has joined a 100ms Room.
The "Behaviours" on the right of the Table shows what happens when the App transitions to Background.
| Scenario | Behaviours |
|---|---|
| Mic is unmuted | Mic will remain Unmuted and the user will able to publish audio without any restriction |
| Camera is unmuted | Camera will get Muted |
| Remote Peers are publishing audio | Incoming Audio from Room Continues to Play |
Android Background Handling
On Android devices, by default Capturing Video & Audio from Camera & Microphone is allowed for sometime - usually 60 seconds. This time limit depends on different Android OEMs, Battery Optimisations Mode (Aggressive/Doze), etc. This leads to inconsistent behaviours of your apps in Background Mode on different Android devices.
As per your use-case, apps can choose to implement an Android Foreground Service to ensure consistent behaviour. With a Foreground Service, you can continuously access Microphone & Camera & publish the captured Audio & Video to other peers in the Room.
Foreground Services show a status bar notification, so that users are actively aware that your app is performing a task and is consuming system resources.
Note: Playing Audio continuously while app is in Background is allowed by default on Android devices.
Without Android Foreground Service (Default Android Behaviour)
The table below lists down Android app behaviours when the app transitions to background when a 100ms Room is ongoing without using any Android Foreground Service.
The "Scenario" on the left of the Table below implies the activity which is ongoing in the App when user has joined a 100ms Room.
The "Behaviours" on the right of the Table shows what happens when the App transitions to Background.
| Scenario | Behaviours |
|---|---|
| Mic is unmuted | Mic will remain Unmuted and the user will able to publish audio for a limited period (time depending on OEMs) |
| Camera is Unmuted | Camera will remain Unmuted and the user will able to publish video for a limited period (time depending on OS) |
| Remote Peers are publishing audio | Able to play incoming audio from the Room |
With Android Foreground Service
When your app implements a Foreground Service it continues access to capturing Audio & Video even when the app is in Background Mode.
| Scenario | Behaviours |
|---|---|
| Mic is unmuted | Mic will remain unmuted and the user will able to publish audio without any restriction |
| Camera is unmuted | Camera will remain unmuted and the user will able to publish video without any restriction |
| Remote Peers are publishing audio | Able to play incoming audio from the Room |
For implementing a Foreground Service we recommend using the flutter_foreground_task package which allows the app to run in the background with a Persistent Status Bar Notification.
Here is step by step guide how to integrate flutter_foreground_task in your apps -
Add plugin
Add flutter_foreground_task as a dependency in your pubspec.yaml file.
dependencies: flutter_foreground_task:
Adding Service in
Depending on your use-case, your app may want either access to microphone or camera or both when the app is in Background. Ensure that you set the correct foregroundServiceType inside the <activity>.
Add service inside <application> tag as follows:
<manifest package="...."> <!-- This is required if the application uses foreground service for android 14 and above--> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_CAMERA"/> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_MICROPHONE" /> <application> ... <activity> ... </activity> // Set Service Type to capture Audio or Video as per your use-case. In most cases, only `microphone` access would be required. Then do not pass the `camera`. If stopWithTask set to true then it will stop the notification if app is force killed. <service android:name="com.pravera.flutter_foreground_task.service.ForegroundService" android:foregroundServiceType="camera|microphone" android:stopWithTask="true" android:exported="false" /> </application>
Initialize Foreground Service
Initialize the FlutterForegroundTask in initState() and Wrap your Meeting page with WithForegroundTask widget. The page which is shown when an 100ms Room is joined should be encapsulated as shown below:
void initState() { super.initState(); // Call FlutterForegroundTask init method. _initForegroundTask(); } void _initForegroundTask() { FlutterForegroundTask.init( androidNotificationOptions: AndroidNotificationOptions( channelId: '100ms_flutter_notification', channelName: '100ms Flutter Notification', channelDescription: 'This notification appears when the foreground service is running.', channelImportance: NotificationChannelImportance.LOW, priority: NotificationPriority.LOW, iconData: const NotificationIconData( resType: ResourceType.mipmap, resPrefix: ResourcePrefix.ic, name: 'launcher', )), iosNotificationOptions: const IOSNotificationOptions(showNotification: false), foregroundTaskOptions: const ForegroundTaskOptions()); } Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( /// A widget that prevents the app from closing when the foreground service is running. /// This widget must be declared above the [Scaffold] widget. home: WithForegroundTask( child: MeetingPage() ); ); }
Start Foreground Service
Start FlutterForegroundTask at onJoin callback.
void onJoin({required HMSRoom room}) async { // Start FlutterForegroundTask at onJoin callback. FlutterForegroundTask.startService( notificationTitle: "100ms foreground service running", notificationText: "Tap to return to the app"); ... }
Stop Foreground Service
Stop FlutterForegroundTask at onRemovedFromRoom and onSuccess -> HMSActionResultListenerMethod.leave callbacks.
class Meeting implements HMSActionResultListener{ void leave(){ //this is the instance of class implementing HMSActionResultListener await hmsSDK.leave(hmsActionResultListener: this); } void onRemovedFromRoom({required HMSPeerRemovedFromPeer hmsPeerRemovedFromPeer}) { // Clear the local room state // Stop FlutterForegroundTask FlutterForegroundTask.stopService(); ... } void onSuccess({HMSActionResultListenerMethod methodType = HMSActionResultListenerMethod.unknown, Map<String, dynamic>? arguments}) { switch (methodType) { case HMSActionResultListenerMethod.leave: // Room leaved successfully // Clear the local room state // Stop FlutterForegroundTask FlutterForegroundTask.stopService(); break; ... } }
That's it. Now you'll have a Foreground Service up & running in your app.
Checkout Background Handling in Action (Video)
-
The attached video shows the fully featured 100ms Example App using Android Foreground Service when a Room starts & ends
-
The Android Foreground Service is started when a Room starts. Similarly, the service is stopped when a Room ends.
-
This ensures that microphone access is available to app even in Background Mode after 60+ seconds.
-
Using Android Foreground Service ensures consistent behaviour on all different devices of Android OEMs like Samsung, Xiaomi, OnePlus, Motorola, Google, etc.
Checkout the Background Handling implementations in 100ms Example app here.
To know more about Android flutter_foreground_task package, visit here.



